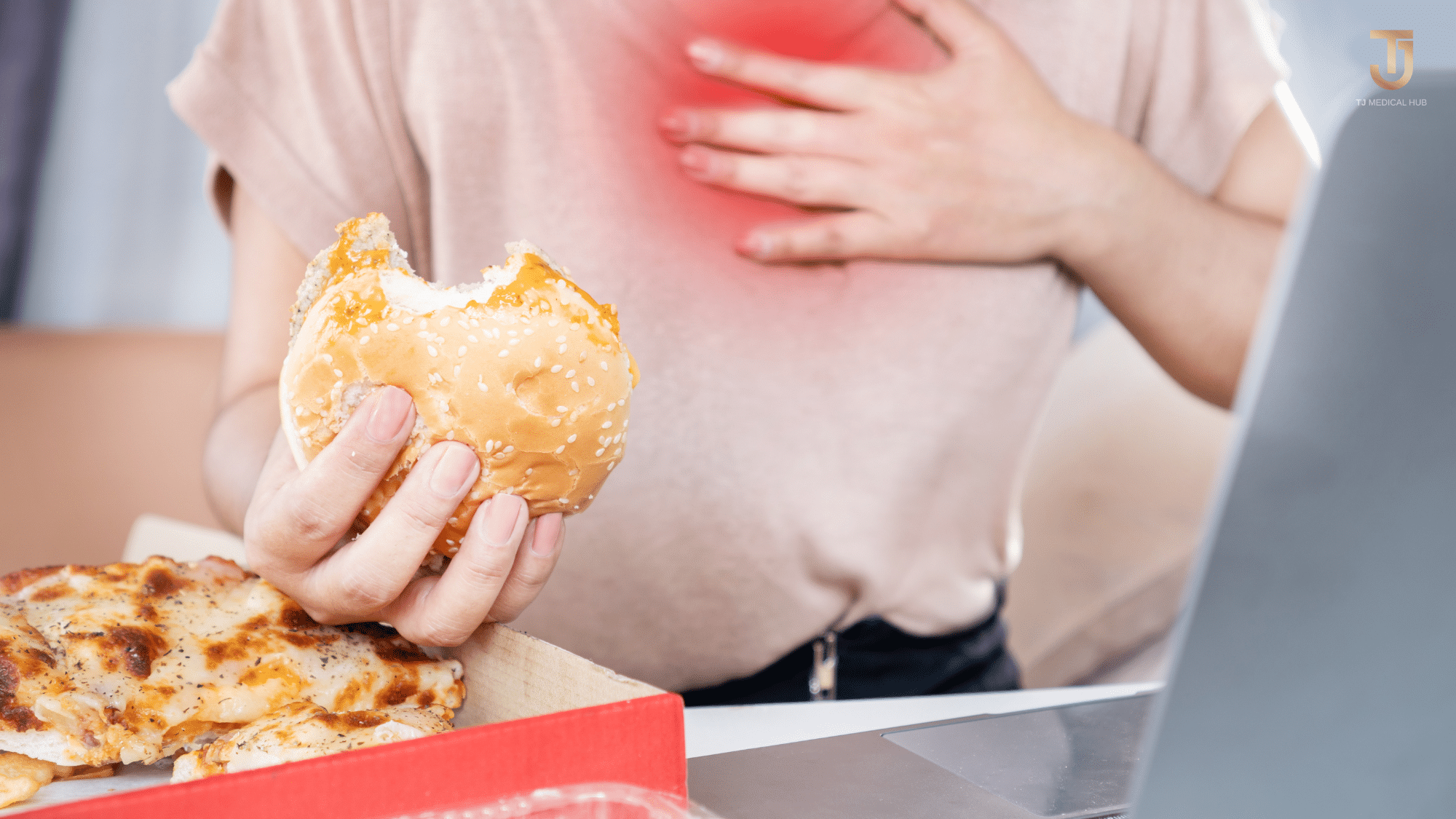
Chest pain, commonly known as heartburn, refers to the discomfort or actual pain resulting from digestive acid flowing into the tube that transports swallowed food to the stomach (esophagus). Key characteristics of heartburn encompass a burning sensation in the chest, potentially extending to the upper abdomen. This sensation typically arises after eating or when lying down or bending over.
Chest pain or discomfort is a symptom often associated with a heart attack, yet it may also indicate other conditions. Asking yourself these questions can assist in determining whether your symptoms necessitate immediate medical attention or warrant scheduling an appointment with a doctor. This article will provide you with advice on the causes of chest pain. Let’s explore together.
Why does my chest hurt after eating?

Indulging in excessive or consuming greasy and spicy foods can lead to a burning sensation in your chest, indicative of heartburn—a symptom associated with acid reflux stemming from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Dr. Caitlin Houghton, a general surgeon at Keck Medicine of USC and assistant professor of clinical surgery at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, emphasizes, “30%-40% of patients presenting to the ER with chest pain attribute their discomfort to acid reflux or GERD.” However, she underscores the importance of recognizing that “heartburn can also be a manifestation of heart problems, warranting assessment by an emergency room or local doctor.”
GERD is a chronic condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. This backflow can result in symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. Lifestyle factors, such as dietary choices, can contribute to the development or exacerbation of GERD.
While occasional heartburn is common and manageable, persistent or severe symptoms may require medical attention. Seeking advice from a healthcare professional can help determine an appropriate course of action, including lifestyle modifications, medications, or further diagnostic evaluation.
How do I know if my chest pain is serious?
Chest pain can have various causes, ranging from benign to serious. It’s essential to pay attention to certain factors that may indicate more serious issues. Here are some signs that your chest pain might be serious, and you should seek medical attention:
- Intensity of Pain: If the pain is severe, persistent, or crushing, it could be a sign of a heart-related issue.
- Duration: If the pain lasts for more than a few minutes or comes and goes over an extended period, it may be a cause for concern.
- Radiation of Pain: Pain that spreads to your arms, neck, jaw, shoulders, or back could be indicative of a heart problem.
- Associated Symptoms: Symptoms such as shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or lightheadedness accompanying chest pain may suggest a serious condition.
- Risk Factors: If you have a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, or other risk factors, chest pain should be taken seriously.
- Age and Gender: Men and women may experience different heart attack symptoms. While men often have classic symptoms, women may experience subtler signs like fatigue, shortness of breath, or nausea.
- Medical History: If you have a personal or family history of heart disease, it increases the likelihood that chest pain could be heart-related.
How often should chest pain after eating be a cause for concern?
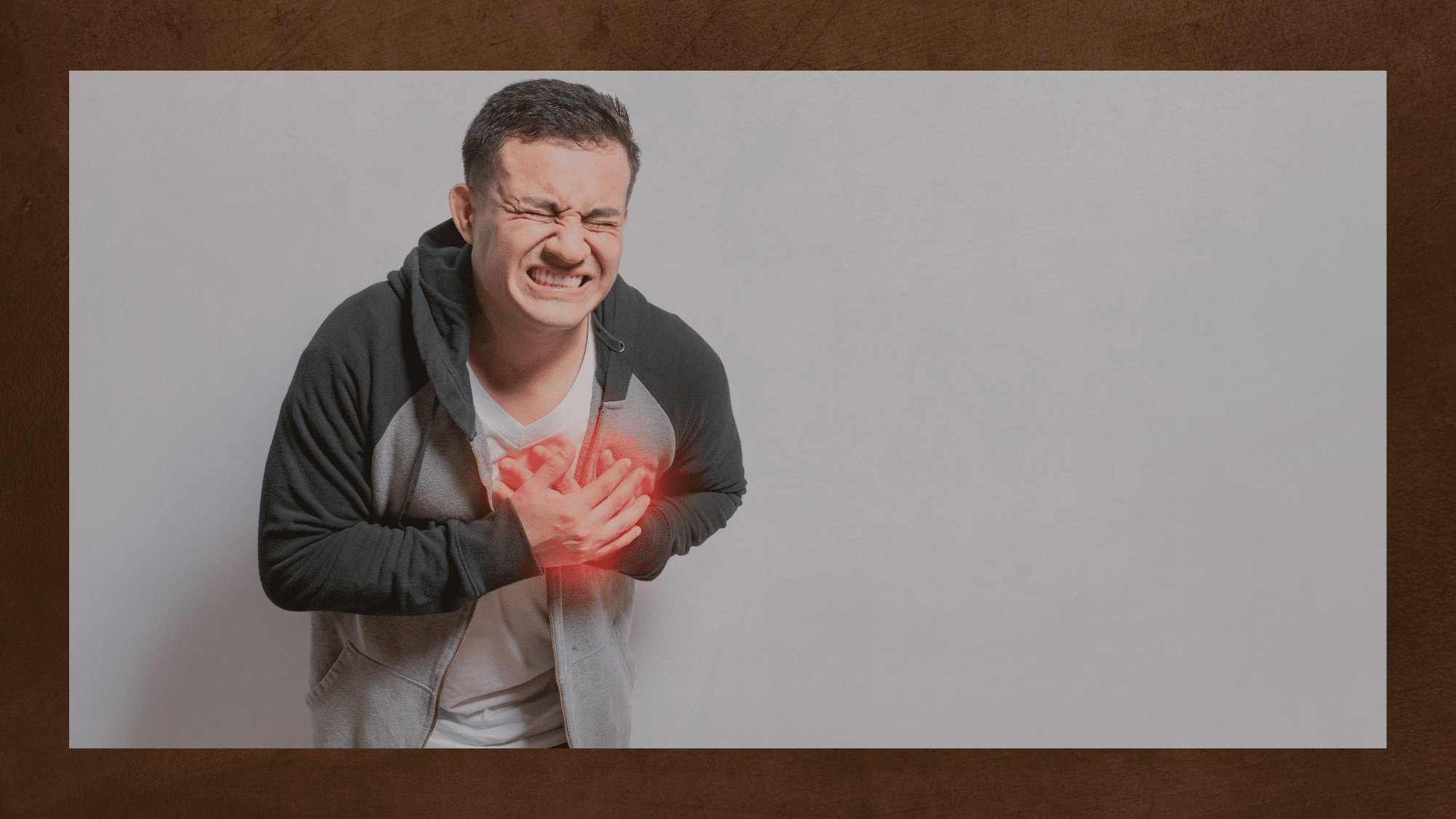

Occasional chest pain after eating may be benign and related to dietary choices. However, if the symptoms are frequent, severe, or accompanied by other concerning signs, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly.
Intermittent heartburn is a commonplace occurrence and generally not a cause for concern. Many individuals can effectively address the discomfort associated with heartburn through self-managed lifestyle adjustments and over-the-counter medications. However, if heartburn becomes more frequent or disrupts your daily activities, it could be indicative of a more serious underlying condition that warrants medical attention.
Why do I experience chest pain after eating?
Chest pain after eating can stem from various causes, including indigestion, heartburn, or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It’s essential to identify the specific symptoms and consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
What lifestyle changes can help alleviate chest pain after eating?
Simple lifestyle modifications such as avoiding spicy or greasy foods, eating smaller meals, and maintaining an upright posture after meals can often alleviate mild symptoms of chest pain after eating. However, individual responses may vary, and consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice is recommended.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for chest pain after eating?
If chest pain after eating is sudden, intense, and accompanied by symptoms like radiating pain to the jaw or left arm, nausea, dizziness, sweating, or shortness of breath, it’s crucial to call emergency services (911) immediately.
Can chest pain after eating be a sign of a more serious condition?
Yes, persistent or severe chest pain after eating could be a symptom of a more serious condition, such as GERD or even cardiac issues. Seeking medical evaluation is essential to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Bariatric surgery, while offering transformative benefits, also comes with potential risks and complications. It’s crucial to be aware of these factors before considering such a procedure. Some potential risks include:
- Infection: Surgical procedures carry a risk of infection at the incision sites or within the abdominal cavity.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery is a potential complication that may require additional medical attention.
- Blood Clots: Surgery increases the risk of blood clot formation, which can potentially lead to serious complications like pulmonary embolism.
- Dumping Syndrome: Rapid emptying of the stomach contents into the small intestine, known as dumping syndrome, can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Malnutrition: Changes in the digestive system can impact nutrient absorption, leading to malnutrition over time.
- Emotional and Psychological Effects: Some individuals may experience emotional challenges, including depression or body image issues, following surgery.
Risk of chest hurts after eating
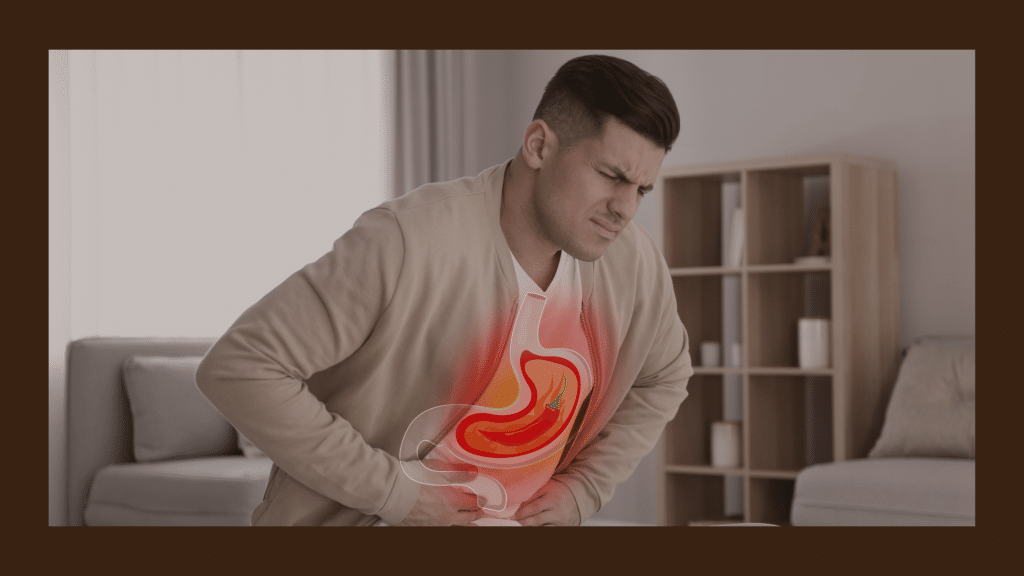

What does heartburn feel like? Experiencing chest pain after eating can be attributed to various factors, and while many cases are benign, some may pose risks or indicate underlying health issues. Here are potential risks associated with chest pain after eating:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
- Risk: Persistent chest pain after eating may signal GERD, a chronic condition where stomach acid regularly flows back into the esophagus.
- Consequence: Over time, untreated GERD can lead to complications like esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, or respiratory problems.
- Heart Issues:
- Risk: Chest pain after eating could indicate heart-related problems, such as angina or a heart attack.
- Consequence: Ignoring potential cardiac issues can lead to serious health complications. Prompt medical attention is crucial to rule out heart-related concerns.
- Peptic Ulcers:
- Risk: Chest pain after eating may be linked to peptic ulcers, which are sores in the stomach lining.
- Consequence: If left untreated, peptic ulcers can cause bleeding, perforation, or obstruction in the digestive tract.
- Gallbladder Issues:
- Risk: Gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder can cause chest pain after eating.
- Consequence: Complications may arise, leading to gallbladder infection or pancreatitis.
- Esophageal Disorders:
- Risk: Conditions like esophageal spasms or motility disorders may contribute to chest pain after eating.
- Consequence: Untreated esophageal disorders may result in difficulty swallowing or damage to the esophagus.
- Pancreatitis:
- Risk: Inflammation of the pancreas can lead to chest pain, particularly after consuming fatty meals.
- Consequence: Severe pancreatitis can cause complications, including organ failure.
It’s essential to recognize that chest pain after eating can have various causes, and the risks associated with it depend on the underlying condition. Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management, especially if the chest pain is severe, persistent, or associated with other concerning symptoms. Always consult with a healthcare professional to assess your individual situation.


