Duodenitis refers to the inflammation of the duodenum, the initial section of the small intestine that connects to the stomach. This condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and other digestive issues, affecting the overall well-being of an individual. The predominant factor leading to duodenitis is the infection caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria. Additionally, prolonged usage of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen is another frequent cause. While less common, other factors should also be considered.
Several factors can contribute to the development of duodenitis. Common causes include. So, Join TJ Medical Hub today as we delve into the comprehensive study of Duodenitis, providing valuable insights for readers keen on understanding this medical condition.
Duodenitis
Duodenitis is characterized by inflammation in the lining of the duodenum. The primary culprits behind duodenitis are often infections caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria. Additionally, extended use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen constitutes another prevalent cause.
What Is the Duodenum?

1. Duodenum Overview
The duodenum, situated just beyond the stomach, is the initial segment of the small intestine responsible for breaking down and digesting food.
2. Chyme Processing
It receives chyme, a semi-fluid mix of partially digested food fibers, from the stomach and employs enzymes and intestinal juices to break it down. These digestive substances are secreted by the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas.
3. Role of Enzymes and Juices
Enzymes and juices from the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas aid in the breakdown of chyme, ensuring proper digestion of starches and fats.
4. Duodenal Hormones
The duodenum releases hormones crucial for digestion, including:
- Secretin:
- Neutralizes duodenal acid by prompting the release of sodium bicarbonate and water, essential for optimal functioning of pancreatic enzymes.
- Cholecystokinin:
- Released during protein and fat consumption, it regulates stomach emptying, stimulates the gallbladder to release bile, and aids in breaking down fats into fatty acids.
5. Nutrient Absorption
The small intestine, primarily the jejunum, facilitates the absorption of vitamins and nutrients from digested food into the bloodstream. Notably, iron absorption occurs in the duodenum.
6. Inflammation and Digestive Impact
Inflammation in the duodenal lining can disrupt the digestive process and hinder the absorption of nutrients, potentially causing complications in nutrient utilization by the body.
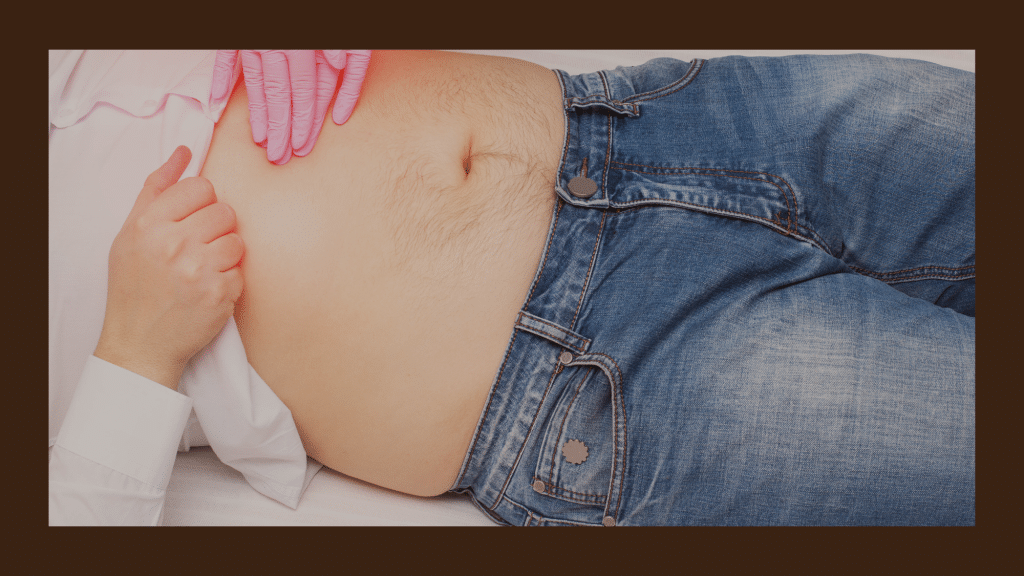
Duodenitis Symptoms
Duodenitis, characterized by inflammation in the lining of the duodenum, manifests with a range of symptoms that can impact an individual’s digestive well-being. Common duodenitis symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain:
- Dull, burning, or cramp-like pain in the upper abdomen is a prevalent symptom of duodenitis.
- Nausea and Vomiting:
- Individuals with duodenitis may experience feelings of nausea, and in severe cases, vomiting may occur.
- Bloating and Gas:
- Excessive gas and a sensation of abdominal bloating are common symptoms associated with duodenal inflammation.
- Indigestion:
- Duodenitis often leads to discomfort and a sense of fullness after eating, contributing to indigestion.
- Changes in Bowel Habits:
- Some individuals may experience alterations in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation.
It’s crucial to note that the severity and combination of these symptoms can vary among individuals. If you suspect duodenitis or experience persistent discomfort, it is advisable to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can contribute to effective management and improved quality of life.
Causes of Duodenitis
Duodenitis, marked by inflammation in the lining of the duodenum, can be attributed to various factors. The primary cause is often the infection by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria, which can irritate and inflame the duodenal lining. Prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen stands as another common culprit, contributing to irritation and inflammation.
While these two causes are prevalent, it’s essential to recognize that other factors can also play a role in the development of duodenitis. Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to duodenal inflammation, and the habit of smoking tobacco may exacerbate the condition. Additionally, chronic stress, though not a direct cause, can potentially contribute to the manifestation of symptoms in individuals predisposed to duodenal inflammation.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of duodenitis causes is crucial for both prevention and effective management. Individuals experiencing symptoms or at risk of duodenitis should consult with healthcare professionals to determine the specific cause and tailor an appropriate treatment plan.
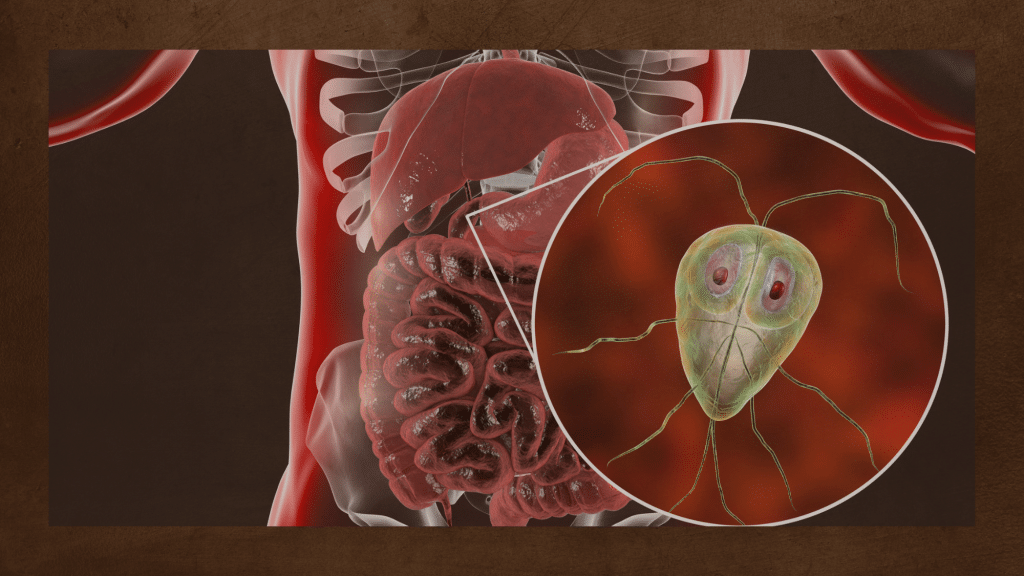
Infection is a leading factor in duodenitis, with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria being the primary culprit. Many individuals harbor H. pylori in the stomach, often acquired during childhood and persisting throughout life. In some cases, the balance of this bacteria can be disrupted. When H. pylori overgrowth occurs in the stomach, it may lead to infections and conditions, such as peptic stomach ulcers. The bacteria can also migrate from the stomach to the duodenum, potentially causing peptic ulcers in this region as well.
Duodenitis Diagnosis
If duodenitis is suspected by your healthcare provider, a series of diagnostic tests, including advanced imaging and blood analyses, may be conducted for a comprehensive assessment. These may involve an upper endoscopy, a procedure utilizing a camera inserted through the throat to examine the duodenum and collect biopsies to detect Helicobacter pylori. Stool samples may be analyzed to identify potential infections, while blood tests may screen for conditions like Celiac disease. Additionally, an upper gastrointestinal series, utilizing X-ray tests and breath assessments, may be employed to scrutinize the upper digestive tract and ascertain the presence of H. pylori.
How serious is duodenitis?
The seriousness of duodenitis can vary widely depending on several factors, including the underlying cause, the extent of inflammation, and how well it responds to treatment. In many cases, duodenitis is a treatable condition, and with appropriate medical intervention, individuals can experience significant relief from symptoms.
However, if left untreated or if the underlying cause is not addressed, duodenitis can potentially lead to complications. Chronic inflammation may result in the development of complications such as peptic ulcers, bleeding, or strictures (narrowing of the digestive tract). These complications can contribute to more severe symptoms and may require more intensive medical management.
Duodenitis Treatment
Duodenitis treatment typically involves a multi-faceted approach to address the underlying causes and manage symptoms. Key components include:
- Antibiotics:
- Antibiotics, such as those targeting Helicobacter pylori, are often prescribed to eliminate bacterial infections contributing to duodenitis.
- Acid-Suppressing Medications:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers may be recommended to reduce stomach acid, promoting healing of the duodenal lining.
- Avoidance of Irritants:
- Patients are advised to avoid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), alcohol, and other substances that may exacerbate duodenal inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary changes, stress management, and smoking cessation may be recommended to improve overall digestive health.
- Symptomatic Relief Medications:
- Medications to alleviate specific symptoms, such as antacids for heartburn, may be suggested for comfort.
- Follow-Up Care:
- Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor progress, adjust treatment plans, and address any emerging concerns.
Individuals experiencing symptoms of duodenitis or those diagnosed with the condition should follow their healthcare provider’s guidance for a personalized treatment strategy. Early intervention and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan contribute to effective management and improved quality of life.