A stroke is a type of brain injury. When this injury occurs in areas that regulate functions such as memory, problem-solving, concentration, and communication, it can result in confusion. Immediate medical attention is imperative for a stroke, and urgent treatment is essential. The sooner an individual receives treatment for a stroke, the reduced likelihood of significant damage.
TJ Medical Hub, your trusted source for comprehensive health information. In this article, we delve into the critical topic of strokes, exploring the various causes that contribute to this serious medical condition. Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention, early detection, and effective management. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of what leads to strokes and how you can safeguard your health.
What Are the Causes of a Stroke?
The primary symptoms of a stroke can be easily recalled using the acronym FAST:
- F – Face: One side of the face may droop, and the person may struggle to smile, with the mouth or eye appearing to sag.
- A – Arms: In the case of a suspected stroke, the person may experience weakness or numbness in one arm, hindering their ability to lift both arms and maintain them in position.
- S – Speech: Speech may be slurred or garbled, and the individual may struggle to communicate. In some cases, they may be unable to talk despite being awake, and comprehension difficulties may arise.
- T – Time: If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, it is vital to call 999 or, if you are in Thailand, dial 1669 without delay. Swift action is essential in responding to a potential stroke, where time is of the essence.
1. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
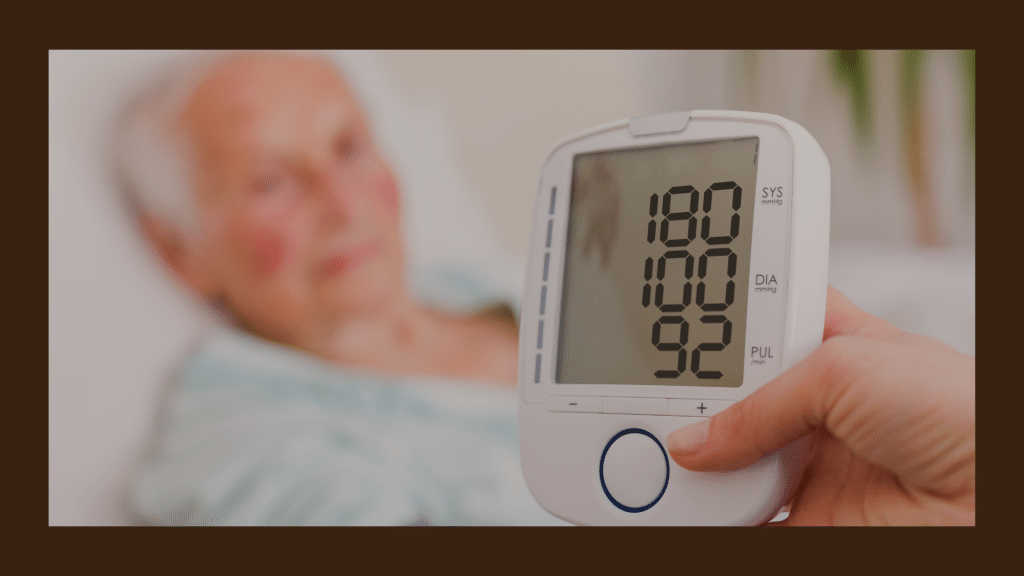
High blood pressure is a leading cause of strokes. The increased pressure within blood vessels can weaken them over time, making them more susceptible to rupture or leakage. Consistent monitoring and management of blood pressure are essential to reduce the risk of stroke.
What is a Category 1 hypertension?
Category 1 hypertension, also known as Stage 1 hypertension, is a classification of high blood pressure according to the blood pressure guidelines. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is recorded as two numbers: systolic over diastolic.
In the context of hypertension categories:
- Normal: Systolic less than 120 mmHg and diastolic less than 80 mmHg.
- Elevated: Systolic 120-129 mmHg and diastolic less than 80 mmHg.
- Category 1 Hypertension (Stage 1): Systolic 130-139 mmHg or diastolic 80-89 mmHg.
- Category 2 Hypertension (Stage 2): Systolic 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic 90 mmHg or higher.
Category 1 hypertension indicates an elevated blood pressure level that may require lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medication, as recommended by healthcare professionals. Regular monitoring and management are essential to reduce the risk of complications associated with high blood pressure. It’s important for individuals with Category 1 hypertension to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
2. Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Irregular heartbeats, known as atrial fibrillation, can lead to blood clots that travel to the brain, causing a stroke. Understanding and managing AFib through medication or other interventions is crucial for stroke prevention.
What does less than 2% AFib mean?
When it’s mentioned that “less than 2% AFib,” it typically refers to the percentage of time or occurrence of atrial fibrillation (AFib) within a given population, context, or study. AFib is an irregular and often rapid heart rate that can lead to various cardiovascular complications.
In this context:
AFib occurrence below 2%” indicates that, in the specified group or scenario, the prevalence of atrial fibrillation is less than 2% of the total. A lower percentage signifies less frequent instances of AFib, whereas a higher percentage indicates a higher frequency. Notably, your AFib History won’t register as 0% but rather as 2% or less. To further understand, you can tap “Show Life Factors” to compare a Life Factor with your AFib History.
3. Smoking and Tobacco Use

Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage blood vessels and contribute to the formation of blood clots. Quitting smoking is a significant step toward reducing the risk of stroke and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Moreover, the dangers of smoking extend beyond cardiovascular health. Smoking is a major contributor to lung cancer, a devastating disease that claims numerous lives each year. If you’re considering quitting smoking, not only will you be safeguarding your heart health, but you’ll also be taking a crucial step in reducing your risk of lung cancer. For more information on the link between smoking and lung cancer, explore our dedicated page on Lung Cancer. Your commitment to quitting is an investment in a healthier, cancer-free future.
How is tobacco related to stroke?
- Damage to Blood Vessels: Tobacco smoke contains numerous harmful chemicals, including nicotine and carbon monoxide. These substances can damage the inner lining of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis). Atherosclerosis narrows and stiffens arteries, reducing blood flow to the brain and increasing the risk of stroke.
- Blood Clot Formation: Smoking can trigger the formation of blood clots. The damaged blood vessels, combined with the increased stickiness of blood platelets caused by smoking, create an environment conducive to clot formation. These blood clots can travel to the brain, leading to a blockage of blood vessels and causing an ischemic stroke.
- High Blood Pressure: Smoking is known to raise blood pressure. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke, as it puts increased stress on blood vessel walls. Over time, this can lead to vessel damage, increasing the likelihood of a stroke.
- Contribution to Other Risk Factors: Smoking often coexists with other stroke risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol. The combination of these risk factors further amplifies the overall risk of stroke.
4. Diabetes
Diabetes increases the risk of stroke by affecting the blood vessels’ integrity and promoting the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Proper diabetes management, including medication, diet, and exercise, is vital for stroke prevention.
Can diabetes lead to a stroke?
Yes, Diabetes markedly elevates the risk of stroke due to its intricate impact on the cardiovascular system. Characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, diabetes directly influences blood vessels, inducing pathological changes that can lead to stroke, especially when cerebral vessels are affected. The well-established association between diabetes and stroke is compounded by the heightened mortality rates and poorer poststroke outcomes observed in individuals with uncontrolled glucose levels. Effectively managing diabetes becomes paramount in mitigating the risk of stroke and improving overall health outcomes.
5. High Cholesterol
Elevated levels of cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of stroke. A balanced diet, exercise, and medication, if necessary, can help control cholesterol levels.
What level of cholesterol can cause stroke?
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often termed the “bad cholesterol” due to its capacity to harm the heart and brain, significantly contributes to the formation of arterial plaque. Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol, surpassing 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), are associated with an augmented risk of experiencing an ischemic stroke.
6. Physical Inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle contributes to various risk factors for stroke, including obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Regular physical activity is a key element in stroke prevention, promoting overall cardiovascular health. As physical inactivity contributes to declines in various mechanisms that can lead to strokes, it has been approximated that it could serve as the primary preventive measure for 10%–30% of strokes, contingent on the level of physical activity engaged in.
Can physical inactivity cause a stroke?
Yes, physical inactivity can contribute to an increased risk of stroke. Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining overall cardiovascular health, and its absence can lead to several risk factors associated with strokes. Here’s how physical inactivity can be linked to stroke risk
- Obesity: Lack of physical activity is a significant contributor to obesity. Being overweight or obese increases the risk of various health issues, including hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol, all of which are risk factors for stroke.
- Hypertension: Physical inactivity is associated with higher blood pressure levels. Hypertension is a well-established risk factor for stroke, as it puts increased stress on blood vessel walls and can lead to their damage over time.
- Diabetes: Physical inactivity is linked to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism, contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, in turn, increases the risk of stroke.
- Atherosclerosis: Regular physical activity helps maintain healthy blood vessels. Inactivity can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of blood clots that can cause a stroke.
- Overall Cardiovascular Health: Physical activity is essential for promoting good cardiovascular health. Inactivity can result in poor circulation, weakened heart muscles, and other cardiovascular issues that may contribute to stroke risk.
Preventing a stroke
To lower your stroke risk: eat well, exercise regularly, limit alcohol, quit smoking. Manage health conditions with prescribed medications for optimal prevention. Especially crucial after a previous stroke.


