Gastric ulcers, lesions on the stomach lining, can be a contributing factor to stomach noises. This condition can manifest as diarrhea and may lead to abdominal discomfort. Accompanying symptoms might include nausea and vomiting.
While some individuals may experience stomach rumbling without other overt symptoms, others might encounter intermittent abdominal pain in the epigastric region, particularly postprandial or nocturnally. Diarrhea or abdominal pain is commonly reported by patients.

Stomach Noises
The pathogenesis of these stomach noises can be attributed to injury to the gastric mucosal cells. This damage may be precipitated by factors such as stress, tobacco use, alcohol consumption, intake of zinc-containing pain relievers, or aspirin, especially in individuals with a history of chronic stress or smoking.
In cases with severe symptoms, there may be an obstruction in the passage of food from the anus to the colon. Predominantly, malignancies in the gastrointestinal tract, like esophageal cancer or tumors situated between the esophagus and the abdomen, can be the underlying causes. Other potential causes encompass colon cancer, colonic ulcers, or masses adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract that may obstruct digestion.
Common symptoms observed in individuals with gastritis that poses a risk for cancer include:
- Distension and delayed gastric emptying.
- Dysphagia.
- Diarrhea or irregular bowel movements.
- Nausea, vomiting, and hemoptysis.
- Abdominal discomfort and cramping.
- Rapid, unexplained weight loss.
These symptoms can manifest in both genders and across all age groups.
If you exhibit these symptoms, it is imperative to seek medical consultation for an accurate diagnosis and therapeutic strategy. Interventions might encompass surgical procedures or pharmacological treatments to enhance the digestive function. Adherence to medical guidance is paramount to ensure patient safety and expedite recovery. The foundation of effective treatment is an accurate diagnosis followed by consistent and appropriate care.
Gastric cancer
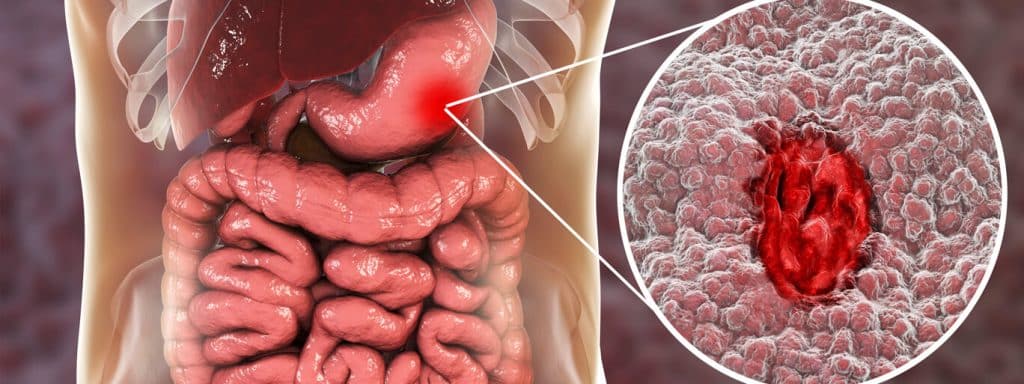
Gastric cancer arises from the uncontrolled proliferation of cells lining the stomach, which can compromise the organ’s functional integrity. Furthermore, this malignancy can metastasize to various other organs, including the intestines, liver, pancreas, and lymph nodes.
Risk Factors for Gastric Cancer
Gastric cancer arises from the uncontrolled proliferation of cells lining the stomach, which can compromise the organ’s functional integrity. Furthermore, this malignancy can metastasize to various other organs, including the intestines, liver, pancreas, and lymph nodes.
- A medical history of stomach ulcer disease.
- Exposure to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
- A history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Chronic gastritis.
- Occupational or environmental exposure to dust and specific chemicals.
- Being overweight, particularly for males (evidence regarding the risk for females remains inconclusive).
- A family history of gastric cancer.
- Lifestyle factors including:
- Regular smoking or prolonged exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Alcohol consumption.
- Regular consumption of processed, fermented, dried, salted, and smoked foods.
- Limited intake of fruits and vegetables.
Treatment for Gastric Cancer
In cases of advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, treatment should be tailored based on the clinical presentation of the disease. Therapeutic options can include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or a combination of both, often administered before surgical intervention. Physicians will determine the most suitable treatment modality and its duration after thorough diagnostic evaluations. It’s essential to note that treatment approaches and responses can vary among individuals based on the disease’s severity and specific symptoms.
Preventive Measures for Gastric Cancer
In cases of advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, treatment should be tailored based on the clinical presentation of the disease. Therapeutic options can include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or a combination of both, often administered before surgical intervention. Physicians will determine the most suitable treatment modality and its duration after thorough diagnostic evaluations. It’s essential to note that treatment approaches and responses can vary among individuals based on the disease’s severity and specific symptoms.
- Daily Health Maintenance: Engage in practices that promote general well-being:
- Manage stress effectively.
- Opt for a balanced diet, incorporating all five food groups in appropriate proportions.
- Limit the consumption of refined and processed foods.
- Abstain from or minimize alcoholic intake.
- Ensure adequate sleep.
- Consistent adherence to these habits can bolster the immune system, reducing susceptibility to a myriad of health conditions.
- Vigilance: To mitigate the risk of gastric cancer, one must be attuned to subtle changes or abnormalities in the body. Symptoms like abdominal discomfort, bloating, early satiety, and indigestion should not be overlooked. Persistent manifestations warrant prompt medical evaluation to ascertain their underlying causes.
- Other Gastrointestinal Concerns: It’s pivotal to understand that not all gastrointestinal symptoms point to gastric cancer. They might be indicative of other conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Neglecting or inadequately managing these conditions can exacerbate their chronicity, subsequently elevating the risk of gastric cancer.
- Routine Health Screening: Regardless of symptomatic presence or absence, regular health check-ups can be instrumental in early detection of potential risks or pathological changes. Timely identification allows for strategic health planning and intervention, significantly enhancing the likelihood of effective treatment and recovery.
Conclusion
In cases of advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, treatment should be tailored based on the clinical presentation of the disease. Therapeutic options can include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or a combination of both, often administered before surgical intervention. Physicians will determine the most suitable treatment modality and its duration after thorough diagnostic evaluations. It’s essential to note that treatment approaches and responses can vary among individuals based on the disease’s severity and specific symptoms.


