Dewormers for Humans, a fundamental component of public health initiatives and personal well-being, is the proactive process of administering medications to eliminate parasitic worms from the human body. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the vital aspects of deworming, providing you with the knowledge needed to understand its importance, the types of parasitic worms that affect humans, the symptoms of parasitic infections, and the available deworming medications and treatment protocols.
As we embark on this journey into the world of Dewormers for Humans, we begin by unraveling the significance of this practice and the potential health risks associated with untreated parasitic infections. By comprehending the essential role deworming plays in preventing the spread of parasites and safeguarding our well-being, we can make informed decisions about our health and contribute to the broader mission of parasite prevention.
Why Dewormers for Humans is Important?
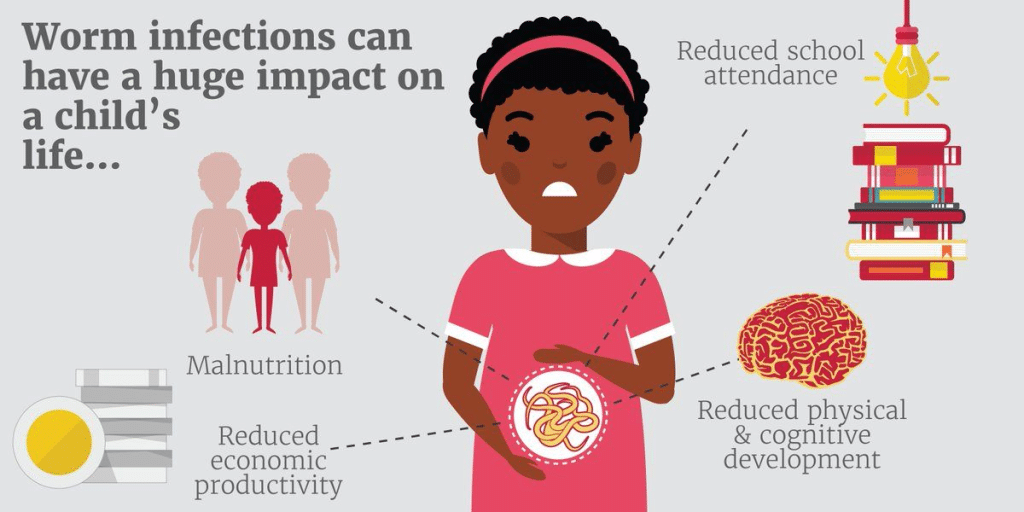
Dewormers for Humans is crucial for both adults and children. If you exhibit signs of worm infestations, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment. Untreated worm infections in adults can result in various health issues, while in children, it can lead to growth impairments and even infant mortality.
The Significance of Dewormers for Humans
Parasitic infections, caused by various types of worms, are a global health concern, affecting millions of people, especially in developing regions. Deworming, the process of administering medications to eliminate parasitic worms from the human body, is a crucial component of public health initiatives and personal well-being. In this section, we’ll delve into why deworming is essential and the potential health risks associated with untreated parasitic infections.
Dewormers for Humans is a proactive measure aimed at curbing the proliferation of parasitic worms within the human body. It offers several critical advantages:
- Preventing Transmission: Many parasitic infections are highly contagious, spreading through contaminated food, water, and soil. By deworming, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of transmitting these parasites to others, thereby limiting the spread of infection within communities.
- Protecting Vulnerable Populations: Children, pregnant women, and individuals with compromised immune systems are particularly vulnerable to parasitic infections. Deworming helps protect these at-risk groups from severe health complications.
- Enhancing Overall Health: Parasitic infections can lead to a wide range of health problems, from nutritional deficiencies and anemia to impaired cognitive development in children. By eliminating parasites, deworming contributes to improved overall health and well-being.
- Boosting Immune Function: Chronic parasitic infections can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to other illnesses. Deworming can help restore the body’s immune function, increasing its ability to fight off infections.
The Health Risks of Untreated Parasitic Infections
The consequences of failing to address parasitic infections can be severe and, in some cases, life-threatening. Untreated parasitic infections can result in:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Parasites often consume essential nutrients in the body, leading to malnutrition, stunted growth, and anemia.
- Digestive Disorders: Many parasites affect the gastrointestinal tract, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- Organ Damage: Some parasites can migrate to organs like the liver, lungs, or brain, causing long-term damage and dysfunction.
- Cognitive Impairment: In the case of children, parasitic infections can impair cognitive development and negatively impact their academic and life prospects.
- Compromised Immunity: Parasites may suppress the immune system, leaving individuals susceptible to other infections and diseases.
Types of Parasitic Worms in Humans
| Tapeworm | Hookworm | Human whipworm |
| Fluke | Ascariasis | Pinworm infection |
| Trichinosis | Tapeworm infection | Cutaneous larva migrans |
Common Parasitic Worms
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, come in various forms and affect millions of people worldwide. Understanding these common parasitic worms is essential for effective prevention and treatment. Let’s delve into some of the most prevalent ones:
Roundworms (Nematodes):
Roundworms, scientifically known as nematodes, are one of the most widespread types of parasitic worms in humans. They include various species, each with its unique health implications. Common roundworm infections include:
- Ascaris lumbricoides: This is the largest roundworm that infects humans. It primarily resides in the small intestine and can lead to symptoms like abdominal pain, malnutrition, and even bowel obstruction.
- Trichuris trichiura (Whipworm): These worms inhabit the large intestine and can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal prolapse in severe cases.
Tapeworms (Cestodes):
Tapeworms, or cestodes, are flat, ribbon-like worms that attach themselves to the wall of the intestines. They consist of a head (scolex) and a chain of segments (proglottids). Common tapeworm infections include:
- Taenia solium (Pork Tapeworm): Consuming undercooked pork infected with the larvae can lead to this tapeworm infection. It can cause digestive disturbances and, in severe cases, neurocysticercosis, a dangerous brain condition.
- Taenia saginata (Beef Tapeworm): Similar to the pork tapeworm, this species is transmitted by consuming undercooked beef containing the larvae.
Flukes (Trematodes):
Flukes, also known as trematodes, are another group of parasitic worms that can affect humans. They have a leaf-like or flattened appearance. Common fluke infections include:
- Schistosoma species: These worms enter the body by penetrating the skin when individuals come into contact with contaminated freshwater. They can cause schistosomiasis, leading to various symptoms, including liver and bladder damage.
Transmission and Life Cycles
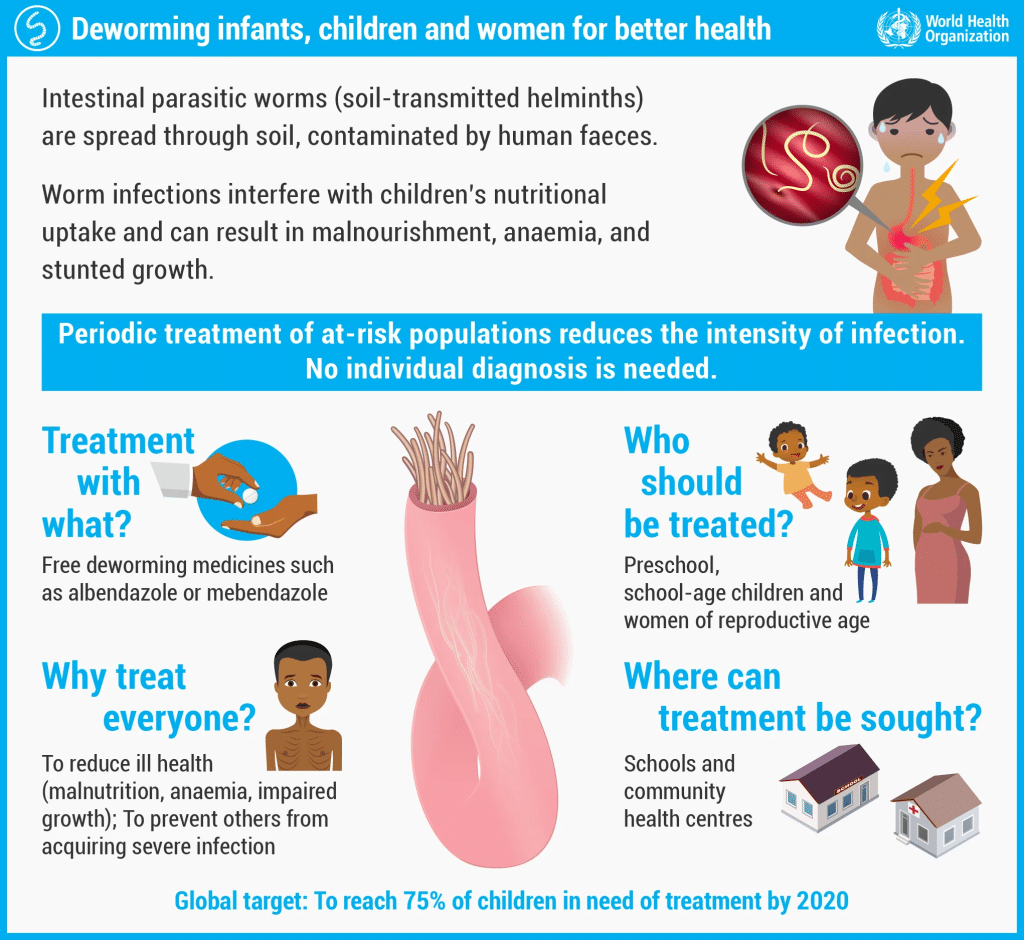
Understanding how parasitic worms are transmitted and their life cycles is critical for effective prevention. The modes of infection and life cycles of these worms can vary, but they generally involve the following:
- Transmission:
- Ingestion: Many parasitic worms, such as roundworms and tapeworms, are often transmitted through the consumption of contaminated food or water. Eggs or larvae in these mediums can lead to infections when ingested.
- Skin Contact: Some parasites, like schistosomes, enter the human body by penetrating the skin upon contact with contaminated freshwater sources.
- Vectors: Certain parasites, such as filarial worms, are transmitted through insect vectors, like mosquitoes or blackflies, which deposit larvae during their blood-feeding process.
- Life Cycles: Parasitic worms have intricate life cycles involving different stages and hosts. For instance:
- Direct Life Cycle: In roundworms like Ascaris, eggs passed in human feces can develop into infectious larvae in the environment, which are then ingested by another host.
- Indirect Life Cycle: Tapeworms, on the other hand, typically involve two hosts—the primary host where adult worms live (humans) and an intermediate host where larvae develop (e.g., pigs or cattle).
- Complex Life Cycle: Parasites like Schistosoma have complex life cycles, including snails as intermediate hosts. Eggs shed in water hatch into larvae, which then penetrate snails and develop before being released into the water to infect humans.
By comprehending the modes of transmission and life cycles of these parasites, individuals can take informed steps to minimize the risk of infection and, when necessary, seek appropriate medical attention for diagnosis and treatment. In the following sections, we’ll explore the symptoms of parasitic infections and the available deworming medications and treatment protocols.
Symptoms of Parasitic Infections
Recognizing the Signs : Parasitic infections can manifest with a wide range of symptoms, often depending on the type of parasitic worm involved and the location within the body where the infection occurs. Recognizing the signs of these infections is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Below, we enumerate the typical symptoms associated with parasitic infections and differentiate between the symptoms caused by various types of worms.
Common Symptoms of Parasitic Infections:
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Many parasitic infections, particularly those involving roundworms and tapeworms, lead to gastrointestinal symptoms, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and bloating.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss, often due to the parasites consuming essential nutrients or causing reduced appetite, can be a sign of parasitic infections.
- Fatigue: Parasites can lead to fatigue and weakness, sometimes resulting from the body’s immune response to the infection.
- Skin Issues: Certain parasites, like schistosomes, can cause skin rashes, itching, or visible tracks under the skin where larvae migrate.
- Anemia: Some parasitic worms, such as hookworms, feed on blood, potentially causing anemia, which may manifest as paleness, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- Allergic Reactions: In cases of certain parasitic infections, individuals may experience allergic reactions, including hives, itching, and swelling, due to the presence of parasites in the body.
- Organ-Specific Symptoms: Parasites that migrate to specific organs, such as the liver or brain, can cause organ-specific symptoms, including pain, organ dysfunction, and neurological issues.
Differentiating Symptoms by Worm Type:
- Roundworm Infections: Roundworm infections, like those caused by Ascaris, Trichuris, or hookworms, typically result in digestive problems, abdominal pain, and nutrient deficiencies. Severe cases can lead to intestinal blockages, anemia, and developmental issues in children.
- Tapeworm Infections: Tapeworms, such as Taenia species, can cause digestive discomfort, weight loss, and allergic reactions in some cases. Neurocysticercosis, a condition involving tapeworm larvae in the brain, may lead to neurological symptoms.
- Fluke Infections: Fluke infections caused by parasites like Schistosoma often involve skin rashes, itching, and damage to the liver or bladder, depending on the species.
- Filarial Worm Infections: Filarial worms can lead to the development of chronic conditions like lymphatic filariasis, characterized by severe swelling of the limbs, and onchocerciasis, known as river blindness due to its effect on the eyes.
Recognizing these symptoms and understanding the type of parasitic infection involved can aid healthcare providers in making an accurate diagnosis and prescribing the appropriate treatment. In the following sections, we’ll explore the diagnostic methods for parasitic infections and the available deworming medications and treatment protocols, shedding light on effective strategies for managing these infections.
Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections
Accurate diagnosis is a cornerstone of effective treatment for parasitic infections. Different tests and procedures are employed to identify the presence of parasitic worms in the human body, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to the specific parasite and its lifecycle stage. In this section, we will explore the various diagnostic methods used and emphasize the importance of precise diagnosis.
Diagnostic Methods for Parasitic Infections:
- Stool Examination: This is one of the most common methods for diagnosing intestinal parasitic infections. A small sample of stool is examined under a microscope to detect parasite eggs or larvae. Different techniques, such as direct smear, concentration methods, and fecal flotation, are used to enhance the chances of finding parasites.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are employed to diagnose certain parasitic infections. For instance, the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in the blood can indicate infections like filariasis or schistosomiasis.
- Imaging Studies: In cases where parasitic infections may cause organ damage or cyst formation, imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans can be used to visualize the affected areas. This is especially important for diagnosing conditions like neurocysticercosis, where tapeworm larvae accumulate in the brain.
- Skin Biopsy: In cases of skin-invading parasites, a skin biopsy may be necessary to identify the parasites and their life stage. This is often used for conditions like cutaneous larva migrans, where hookworm larvae migrate under the skin.
- Serological Tests: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and other serological tests are utilized to detect antibodies or antigens related to specific parasitic infections. These tests can be valuable for conditions like amebiasis and schistosomiasis.
- Molecular Tests: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA-based tests can identify the genetic material of parasites in clinical samples. These tests are highly specific and can help diagnose infections that may be missed by traditional methods.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis:
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for several reasons:
- Tailored Treatment: Different parasitic infections require specific medications and treatment regimens. Accurate diagnosis ensures that the right treatment is administered, increasing the chances of successful parasite elimination.
- Preventing Misdiagnosis: Many symptoms of parasitic infections overlap with other medical conditions. Precise diagnosis helps prevent misdiagnosis and the unnecessary use of medications.
- Preventing Resistance: Inappropriate use of deworming medications can lead to drug resistance in parasites. Accurate diagnosis helps prevent unnecessary treatment and, consequently, the development of drug-resistant strains.
- Epidemiological Surveillance: Accurate diagnosis contributes to tracking and understanding the prevalence of parasitic infections in different regions, aiding in public health efforts to control these diseases.
In summary, diagnostic methods for parasitic infections are diverse and depend on the type of parasite and the affected organ or system. An accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective treatment, allowing for the targeted elimination of the parasites while minimizing the risk of misdiagnosis or drug resistance. In the following sections, we’ll explore deworming medications and treatment protocols, shedding light on how to address parasitic infections effectively.
Dewormers for Humans medications
When it comes to Dewormers for Humans, there is a spectrum of medications available, each tailored to target specific parasitic worms and their life stages. These deworming medications fall into different classes, with anthelmintics being a prominent category. Here’s an overview of the various deworming medications:
Real-Life Experiences
Anthelmintics: Anthelmintics are the primary class of medications used to treat parasitic worm infections in humans. They are specifically designed to kill or paralyze the worms, facilitating their expulsion from the body. Within the anthelmintic class, there are several subtypes that target different parasites. Common anthelmintic medications include:
- Albendazole: Effective against various parasitic worms, including roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes.
- Mebendazole: Widely used to treat roundworms and some tapeworm infections.
- Ivermectin: Highly effective against certain filarial worms and parasites like scabies mites.
- Praziquantel: Primarily used to treat tapeworm infections, particularly schistosomiasis.
Prescription vs. Over-the-Counter Dewormers
When considering deworming medications, it’s essential to understand the distinction between prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) options. This differentiation can significantly impact the choice of treatment:
Prescription Dewormers: These medications require a prescription from a healthcare provider. They are often reserved for more severe or complex cases of parasitic infections. Medical supervision is necessary to ensure the proper diagnosis, dosage, and monitoring during treatment. Prescription dewormers are typically used when the specific parasite species or resistance patterns need to be considered.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Dewormers: Some deworming medications are available without a prescription. These are generally suited for milder cases of parasitic infections. OTC dewormers can be appropriate for common, easily recognizable parasitic infections, but they may not be as effective against all parasitic species. It’s essential to follow the instructions carefully and, if symptoms persist or worsen, seek professional medical advice.
Safety and Side Effects
While Dewormers for Humans medications are generally safe and effective, there are potential side effects and safety considerations to be aware of. These may include:
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Common side effects include nausea, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea. These symptoms are often mild and short-lived.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, individuals may experience allergic reactions to deworming medications. Signs of an allergic reaction include hives, itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if this occurs.
- Drug Interactions: Some dewormers can interact with other medications you may be taking. It’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are using to avoid potential interactions.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should consult a healthcare professional before taking deworming medications, as their safety during these periods may vary.
In the quest for comprehensive parasite prevention and optimal health, understanding the types and uses of dewormers for humans is an essential component. Through this article, we have explored the intricate world of parasitic infections, shedding light on the significance of deworming, the symptoms that may signal their presence, and the diagnostic methods that lead to effective treatment. As we navigate the terrain of deworming medications, we’ve discovered the diversity of anthelmintics designed to combat specific parasites. Whether prescribed by a healthcare professional or available over-the-counter, these medications play a pivotal role in eradicating parasitic invaders and restoring health.
In closing, “Parasite Prevention: Understanding the Types and Uses of Dewormers for Humans” is not just an article—it’s a roadmap to health, awareness, and a brighter future. By arming ourselves with knowledge, seeking medical guidance when needed, and embracing preventative measures, we can collectively strive towards a world where parasitic infections become a rarity rather than a reality. It’s a journey worth embarking upon, one that leads to healthier lives and healthier communities.
TJ Medical Hub is here to support you every step of the way, providing valuable information and resources to help you on your path to better health and a safer, parasite-free world. Together, we can make this vision a reality, ensuring that both individuals and communities thrive in a world with reduced parasitic infections.


