Are you alarmed by the sight of blood in your sink when you brush or floss your teeth? Bleeding gums can be unsettling, but they’re more common than you might think. Understanding what causes bleeding gums and how to address them is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Let’s delve into this topic and shed some light on what bleeding gums are all about.
What Are Bleeding Gums?
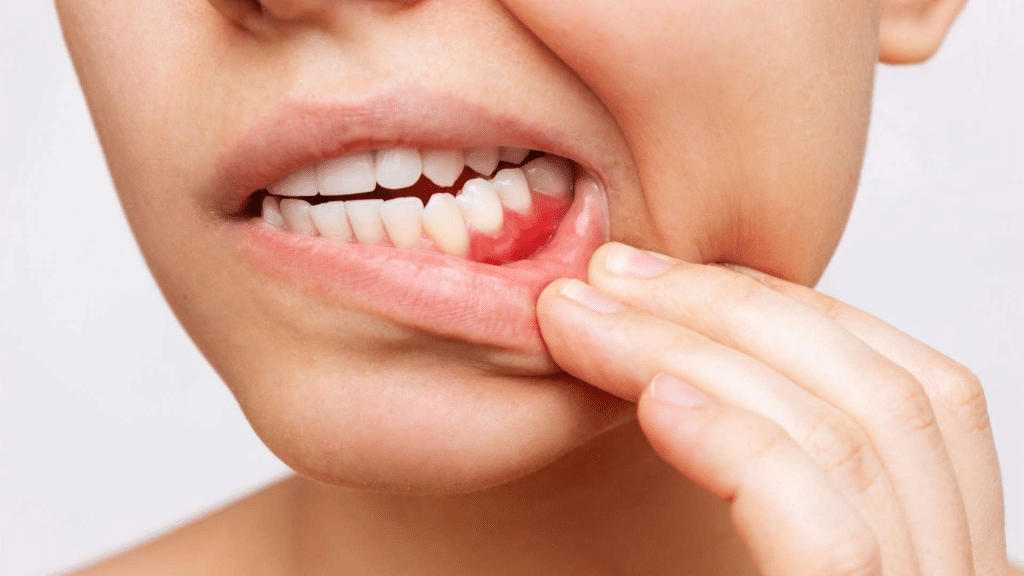
Bleeding gums, medically known as gingival bleeding, occur when blood is released from the gums during activities such as brushing, flossing, or even eating. Healthy gums typically have a firm, pink appearance and should not bleed when touched or brushed. When gums bleed easily, it’s often an indication of underlying issues in oral health.
Anatomy of the Gums:
To understand why gums bleed, it’s essential to grasp the anatomy of the gums. Gums, also called gingiva, are soft tissues that surround and support the teeth. They cover the jawbone and serve as a protective barrier for the tooth roots and underlying bone. The gum tissue is composed of dense fibrous connective tissue containing blood vessels and nerves.
Causes of Bleeding Gums
Several factors can contribute to bleeding gums:
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is often the primary cause of bleeding gums. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates along the gumline due to poor oral hygiene habits. Plaque buildup irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and bleeding. If not addressed, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
- Periodontitis: If left untreated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease. In periodontitis, the infection spreads beneath the gumline, causing pockets to form between the gums and teeth. This leads to further inflammation, gum recession, bone loss, and ultimately, tooth loss.
- Aggressive Brushing or Flossing: Brushing or flossing too vigorously can damage the delicate gum tissue, leading to bleeding. It’s essential to use gentle brushing and flossing techniques to clean teeth effectively without causing irritation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as blood thinners and antihypertensives, can increase the risk of bleeding gums. If you’re experiencing bleeding gums and are taking medication, consult your healthcare provider for guidance on managing this side effect.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can make the gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits are crucial during these times to maintain gum health.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can weaken the gums and make them more susceptible to bleeding. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help support gum health.
Symptoms of Bleeding Gums:
In addition to bleeding during brushing or flossing, other signs and symptoms of bleeding gums may include:
- Swollen or Tender Gums: Inflamed gums may appear red, swollen, and tender to the touch.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Bacteria in the mouth can contribute to bad breath, especially when accompanied by gum disease.
- Receding Gums: As gum disease progresses, the gums may recede, exposing more of the tooth’s root.
- Loose Teeth: Advanced gum disease can cause teeth to become loose or shift in position.
- Changes in Denture Fit: If you wear dentures, you may notice changes in how they fit as gum disease progresses.
Treatment and Prevention
Bleeding gums can be a distressing symptom, but the good news is that with proper care and attention, you can effectively manage and prevent them. Here’s a comprehensive guide on treatment and prevention strategies to promote optimal oral health:
Embrace a Consistent Oral Hygiene Routine: One of the most crucial steps in preventing bleeding gums is maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine. Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Gentle, circular motions are key to effectively removing plaque and debris without causing irritation to the gums. Don’t forget to floss daily to clean between teeth and along the gumline, where a toothbrush may not reach.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular visits to your dentist are essential for detecting and addressing any signs of gum disease early on. Your dentist can perform a thorough examination of your gums, teeth, and overall oral health. Professional cleanings help remove plaque and tartar buildup, reducing the risk of gum inflammation and bleeding. Your dentist can also provide personalized recommendations for improving your oral hygiene routine and addressing any underlying issues contributing to bleeding gums.
Professional Dental Treatments: Depending on the severity of your gum disease, your dentist may recommend additional treatments to help manage bleeding gums. These treatments may include scaling and root planing, which involves a deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooth the tooth roots. Your dentist may also prescribe an antibacterial mouthwash to help control bacterial growth and reduce inflammation in the gums. In more advanced cases, surgical interventions such as flap surgery or gum grafting may be necessary to restore gum health and prevent further complications.
Lifestyle Changes: Certain lifestyle factors can impact the health of your gums. Quitting smoking is crucial, as smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease and can impair the body’s ability to heal damaged gum tissue. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients for gum health. Vitamin C, in particular, plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system and promoting gum healing.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of gum disease. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as exercise, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine can help support overall gum health. Finding healthy ways to manage stress can have a positive impact on both your oral and overall health.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up: After implementing preventive measures and undergoing treatment for bleeding gums, it’s essential to monitor your oral health closely and follow up with your dentist regularly. Be vigilant for any signs of recurrence or worsening symptoms, and don’t hesitate to seek professional dental care if you have concerns. Your dentist can provide ongoing guidance and support to help you maintain healthy gums and teeth for years to come.
Conclusion:
By adopting a proactive approach to oral hygiene, seeking regular dental care, and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can effectively prevent and manage bleeding gums. Remember to prioritize your oral health and take steps to address any concerns promptly. With the right strategies and support from your dentist, you can enjoy a confident smile and optimal oral health for life.


